- Vitamin D and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: SERVE Study (SARS-CoV-2 Exposure and the Role of Vitamin D among Hospital Employees)
- VitaminDWiki – COVID-19 treated by Vitamin D - studies, reports, videos
- There have been
2339 visits to this page
Vitamin D and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: SERVE Study (SARS-CoV-2 Exposure and the Role of Vitamin D among Hospital Employees)
J Nutr. 2023 Mar 3;S0022-3166(23)35280-5. doi: 10.1016/j.tjnut.2023.03.001 behind paywall
Yi Liu 1, Shannon Clare 1, Gia D'Erasmo 1, Alison Heilbronner 1, Alexander Dash 1, Alexandra Krez 1, Caroline Zaworski 1, Katherine Haseltine 1, Alana Serota 2, Andy Miller 3, Keila Veiga 4, Marvin Sandoval Theresa T Lu 4, Donald J McMahon 1, Jeri W Nieves 2, Emily Margaret Stein 5Context: Recognition of the role of vitamin D in immune function has led to interest in its relationship with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Although clinical studies to date have had conflicting results, many individuals currently take high doses of vitamin D to prevent infection. The goal of this study was to investigate the relationships between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD) and vitamin D supplement use with incident SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Methods: In this prospective cohort study 250 healthcare workers were enrolled at a single institution and followed for 15 months. Participants completed questionnaires every 3 months regarding new SARS-CoV-2 infection, vaccination, and supplement use. Serum was drawn at baseline, 6, and 12 months for 25OHD and SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antibodies.
Results: Mean age of participants was 40 years, BMI 26 kg/m2, 71% were Caucasian, and 78% female. Over 15 months, 56 participants (22%) developed incident SARS-CoV-2 infections. At baseline, ∼50% reported using vitamin D supplements (mean daily dose 2250 units). Mean serum 25OHD was 38 ng/ml. Baseline 25OHD did not predict incident SARS-CoV-2 infection (Odds ratio [OR] 0.98, 95% CI 0.80-1.20). Neither use of vitamin D supplements (OR 1.18, 95% CI 0.65-2.14), nor supplement dose was associated with incident infection (OR 1.01 per 100-units increase, 95% CI 0.99 - 1.02).
Conclusion: In this prospective study of health care workers, neither serum 25OHD nor use of vitamin D supplements was associated with incident SARS-CoV-2 infection. Our findings argue against the common practice of taking high dose vitamin D supplements for presumed prevention of COVID-19.
VitaminDWiki – COVID-19 treated by Vitamin D - studies, reports, videos
As of March 31, 2024, the VitaminDWiki COVID page had: trial results, meta-analyses and reviews, Mortality studies see related: Governments, HealthProblems, Hospitals, Dark Skins, All 26 COVID risk factors are associated with low Vit D, Fight COVID-19 with 50K Vit D weekly Vaccines Take lots of Vitamin D at first signs of COVID 166 COVID Clinical Trials using Vitamin D (Aug 2023) Prevent a COVID death: 9 dollars of Vitamin D or 900,000 dollars of vaccine - Aug 2023
5 most-recently changed Virus entries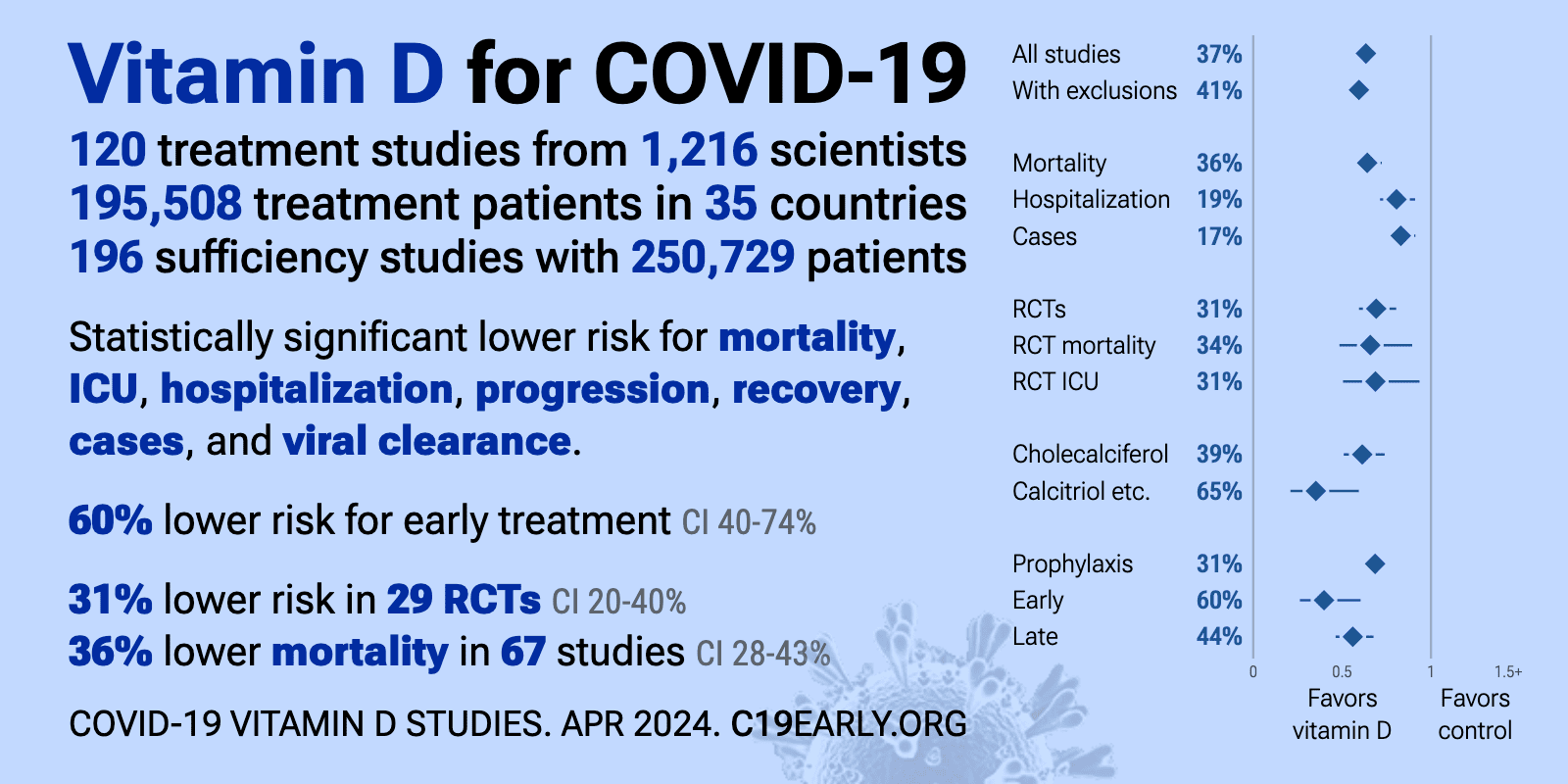
- The above image is automatically updated
There have been
2339 visits to this page COVID not prevented by 2,200 IU daily vitamin D (no surprise) - March 2023(Cached) Printer Friendly Follow this page for updates1343 visitors, last modified 21 Dec, 2023, This page is in the following categories (# of items in each category)
- There have been