Physiology of Vitamin D—Focusing on Disease Prevention
Nutrients 2024, 16, 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111666
Sunil J. Wimalawansa - Cardiometabolic & Endocrine Institute, North Brunswick, NJ 08902, USA; suniljw at hotmaiI.com
Vitamin D is a crucial micronutrient, critical to human health, and influences many physiological processes. Oral and skin-derived vitamin D is hydroxylated to form calcifediol (25(OH)D) in the liver, then to 1,25(OH)2D (calcitriol) in the kidney. Alongside the parathyroid hormone, calcitriol regulates neuro-musculoskeletal activities by tightly controlling blood-ionized calcium concentrations through intestinal calcium absorption, renal tubular reabsorption, and skeletal mineralization.
Beyond its classical roles, evidence underscores the impact of vitamin D on the prevention and reduction of the severity of diverse conditions such as
- cardiovascular and metabolic diseases,
- autoimmune disorders,
- infection, and
- cancer.
Peripheral target cells, like immune cells, obtain vitamin D and 25(OH)D through concentration-dependent diffusion from the circulation.
Calcitriol is synthesized intracellularly in these cells from these precursors, which is crucial for their protective physiological actions. Its deficiency exacerbates inflammation, oxidative stress, and increased susceptibility to metabolic disorders and infections; deficiency also causes premature deaths. Thus, maintaining optimal serum levels above 40 ng/mL is vital for health and disease prevention. However, achieving it requires several times more than the government's recommended vitamin D doses. Despite extensive published research, recommended daily intake and therapeutic serum 25(OH)D concentrations have lagged and are outdated, preventing people from benefiting.
Evidence suggests that maintaining the 25(OH)D concentrations above 40 ng/mL with a range of 40-80 ng/mL in the population is optimal for disease prevention and reducing morbidities and mortality without adverse effects.
The recommendation for individuals is to maintain serum 25(OH)D concentrations above 50 ng/mL (125 nmol/L) for optimal clinical outcomes. Insights from metabolomics, transcriptomics, and epigenetics offer promise for better clinical outcomes from vitamin D sufficiency. Given its broader positive impact on human health with minimal cost and little adverse effects, proactively integrating vitamin D assessment and supplementation into clinical practice promises significant benefits, including reduced healthcare costs. This review synthesized recent novel findings related to the physiology of vitamin D that have significant implications for disease prevention.
Download the PDF from VitaminDWiki
Table of Contents

10 summary points by Perplexity AI (June 2024)
- Vitamin D Metabolism:
Vitamin D is hydroxylated in the liver to form calcifediol (25(OH)D) and then in the kidney to form calcitriol (1,25(OH)₂D), which regulates calcium and phosphorus metabolism essential for bone health.
- Broader Health Implications:
Beyond bone health, vitamin D plays a crucial role in preventing cardiovascular and metabolic diseases, autoimmune disorders, infections, and cancer by modulating immune function and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Optimal Serum Levels:
Maintaining serum 25(OH)D concentrations above 40 ng/mL, with an optimal range of 40-80 ng/mL, is essential for disease prevention and reducing morbidity and mortality. For optimal clinical outcomes, levels above 50 ng/mL are recommended.
- Deficiency and Health Risks:
Vitamin D deficiency, defined as serum 25(OH)D levels below 12 ng/mL, exacerbates inflammation, increases susceptibility to infections and metabolic disorders, and is associated with higher mortality rates.
- Public Health Concern:
Vitamin D deficiency is a widespread issue affecting over half of the global population, particularly those with limited sun exposure. This deficiency is more prevalent than iron deficiency and has significant health implications.
- Current Recommendations:
Government-recommended daily doses of vitamin D (400-1000 IU/day) are insufficient to achieve optimal serum levels. Higher doses are necessary to maintain adequate vitamin D status and prevent various diseases.
- Clinical Signs of Deficiency:
Symptoms of severe vitamin D deficiency include muscle weakness, bone pain, skeletal deformities, increased risk of fractures, and generalized fatigue. These symptoms often overlap with other health conditions.
- Non-Classical Actions of Calcitriol:
Calcitriol synthesized in peripheral target cells, such as immune cells, plays a vital role in immune function, reducing the risk of infections and inflammatory responses. This intracellular synthesis is crucial for its protective actions.
- Genetic Influences:
Genetic factors, such as mutations in the CYP27B1 and CYP2R1 genes, can affect vitamin D metabolism and lead to conditions like rickets. These genetic variations influence the body's ability to synthesize and utilize vitamin D.
- Health Economics:
Addressing vitamin D deficiency through supplementation is cost-effective and can significantly reduce healthcare costs associated with treating diseases linked to vitamin D deficiency. The cost-benefit ratio of prophylactic vitamin D is highly favorable.
7+ VitaminDWiki pages have SUNIL in the title
The list is automatically updated
Items found: 11
|
Title |
|
Modified |
|
Health Benefits of Vitamin D - Sunil April 2025 |
|
07 Apr, 2025 |
|
Vitamin D: Everything You Need to Know - book bu Sunil Aug 2012 |
|
21 Feb, 2025 |
|
Many Chronic Health Diseases and Infections can controlled by 40 ng of Vitamin D – Sunil Aug 2023 |
|
21 Feb, 2025 |
|
Physiological Basis for Using Vitamin D to Improve Health - Sunil May 2023 |
|
21 Feb, 2025 |
|
Skin aging reduced by Vitamin D - Sunil Jan 2025 |
|
21 Jan, 2025 |
|
Vitamin D helps the immune system fight COVID-19 – Sunil video Jan 2021 |
|
30 Aug, 2024 |
|
COVID-19 Vitamin D Overview - Sunil video and transcript - Dec 8, 2020 |
|
30 Aug, 2024 |
|
D3, D2, K2, sun, etc. - Interview and transcript Sunil Aug 2024 |
|
30 Aug, 2024 |
|
Many viral diseases can be fought by immune system-augmented Vitamin D - Sunil Aug 2024 |
|
24 Aug, 2024 |
|
Many diseases prevented if Vitamin D level higher than 50 ng -Sunil June 2024 |
|
02 Jun, 2024 |
|
Fight infections such as COVID with 50 ng of Vitamin D – Sunil Dec 2022 |
|
19 Dec, 2022 |
>100 publications by Sunil in Google Scholar as of June 2024
Half of the people got to 50 ng with 5,000 IU daily
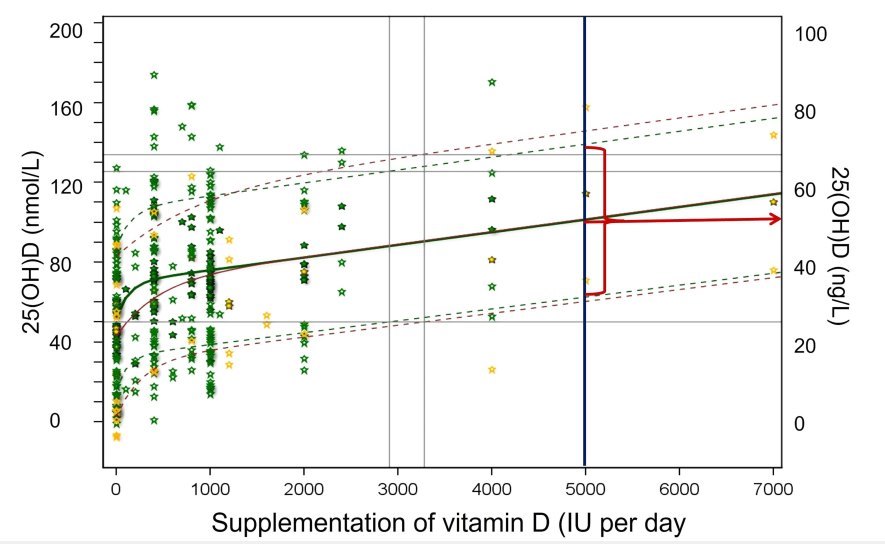
Note: Virtually all will get >40 ng with 7,000 IU daily (50,000 IU weekly)
* Evolution of experiments with patients, often also need co-factors
82+ pages have 50 ng in the VitaminDWiki title
This list is automatically updated
Items found: 90
|
Title |
|
Modified |
|
Osteoporosis in France can be fought with 50,000 IU of Vitamin D, weekly then bi-weekly (30-60ng) - Feb 2025 |
|
21 Feb, 2025 |
|
What's the Optimal Level of Vitamin D (50-60 ng) - Patrick Jan 2025 |
|
15 Jan, 2025 |
|
Type 1 Diabetic inflammation reduced by 50 ng of Vitamin D - Dec 2024 |
|
21 Dec, 2024 |
|
Women were 50X more likely to be fertile if just 1 ng higher level of vitamin D – Nov 2024 |
|
18 Nov, 2024 |
|
Jaw joint (TMJ) needs 30-50 ng of Vitamin D and a good VDR – April 2021 |
|
17 Oct, 2024 |
|
Vitamin D levels jumped during COVID - 2X more had at least 50 ng, 8X more had at least 100 ng – July 2024 |
|
11 Aug, 2024 |
|
Colon Cancer survival increases with vitamin D, up to 50 ng – Aug 2024 |
|
11 Aug, 2024 |
|
In vitro Fertilization not helped if Vitamin D is slightly above 30 ng (need 50 ng) – July 2024 |
|
05 Jul, 2024 |
|
50,000 IU Vitamin D once every 2 weeks – response was 34 ng – RCT April 2017 |
|
12 Jun, 2024 |
|
Many diseases prevented if Vitamin D level higher than 50 ng -Sunil June 2024 |
|
02 Jun, 2024 |
|
Is 50 ng of Vitamin D enough to fight COVID - TrialSiteNews - Jan 2024 |
|
31 Jan, 2024 |
|
50 ng of Vitamin D - 100 hours of noon sunbathing OR 3 dollars of Vit D |
|
05 Aug, 2023 |
|
Cognition improved in 5 ways after Vitamin D increased to 32 ng (50,000 weekly) – June 2023 |
|
03 Jul, 2023 |
|
50 ng level of Vitamin D proven to fight many diseases - Whittle May 2023 |
|
17 May, 2023 |
|
4X reduction in prediabetes progressing to T2D if more than 50 ng of vitamin D – RCT March 2023 |
|
01 May, 2023 |
|
Fight infections such as COVID with 50 ng of Vitamin D – Sunil Dec 2022 |
|
19 Dec, 2022 |
|
Mortality reduced by 35 percent if everyone had 50 ng of vitamin D - Grant Oct 2021 |
|
09 Dec, 2022 |
|
Kidney Inflammation not reduced by 30 ng Vitamin D (many health problems need 50 ng) – Nov 2022 |
|
09 Nov, 2022 |
|
Complement system (part of innate immunity) needs Vitamin D (50 ng is good) – Sept 2022 |
|
01 Oct, 2022 |
|
10,000 IU Vitamin D raised basketball player levels (more than 50 ng need to improve performance) – June 2022 |
|
01 Aug, 2022 |
|
Suggested dosing to get 50 ng of Vitamin D (if healthy) - July 2022 |
|
21 Jul, 2022 |
|
COVID probably fought by Vitamin D, might need 50 ng - Dr. Patrick Nov 8, 2021 |
|
21 Jul, 2022 |
|
Is 50 ng of vitamin D too high, just right, or not enough |
|
14 May, 2022 |
|
COVID-19 mortality extrapolates to zero at 50 ng of vitamin D – 18th Meta-analysis Sept 2021 |
|
18 Mar, 2022 |
|
Optimal Vitamin D level: 50-90 ng - Dr. Vasquez |
|
18 Mar, 2022 |
|
Psoriasis reduced for those getting Vitamin D levels above 50 ng – RCT Feb 2018 |
|
11 Mar, 2022 |
|
See all vitaminDWiki pages with 50...150 AND ng in title |
|
28 Feb, 2022 |
|
Prevent half of T1 Diabetes with vitamin D levels of 50 ng – Dec 2012 |
|
04 Jan, 2022 |
|
Texas town wants employees above 50 ng of Vitamin D to fight COVID-19 - Dec 24, 2020 |
|
26 Nov, 2021 |
|
Discussion of COVID and 50 ng of Vitamin D (video and transcript)– Dr. Campbell Nov 17, 2021 |
|
19 Nov, 2021 |
|
Vitamin D might a risk factor of insulin resistance, diabetes, obesity, etc. (50 ng) – Oct 2021 |
|
26 Oct, 2021 |
|
Vitamin D and COVID, review of evidence, loading dose if less than 50 ng - Masterjohn Sept 2021 |
|
05 Sep, 2021 |
|
Less muscle inflammation after exercise if high level of Vitamin D (50 ng) -July 2021 |
|
08 Jul, 2021 |
|
T-cells need at least 40-50 ng of Vitamin D to fight COVID-19 - June 2021 |
|
01 Jun, 2021 |
|
Little risk of infection after surgery if have more than 50 ng of vitamin D - 2014 |
|
30 May, 2021 |
|
50,000 IU of Vitamin D once every 2 weeks achieved 40 ng in 3 months – RCT March 2021 |
|
24 Apr, 2021 |
|
More than 30 ng of vitamin D is sometimes needed (Kidney needs 50 ng) – March 2019 |
|
31 Mar, 2021 |
|
To protect against COVID-19, how much vitamin D – 20 to 50 ng – March 19, 2021 |
|
23 Mar, 2021 |
|
5000 IU of vitamin D in daily bread resulted in 50 ng and improved quality of life– May 2014 |
|
20 Mar, 2021 |
|
How much vitamin D is needed ( perhaps 50 ng for infections) |
|
08 Mar, 2021 |
|
Influenza prevented by 40 ng levels or treated with vitamin D hammer (50,000 IU) – June 2015 |
|
26 Dec, 2020 |
|
Saudi study defines normal Vitamin D level to be 50 to 70 ng (diabetes, etc.) - June 2020 |
|
12 Dec, 2020 |
|
Diabetes 50X less likely if 30 ng of Vitamin D and intense exercise – April 2018 |
|
11 Nov, 2020 |
|
Only 1 NCAA basketball player getting 10,000 IU vitamin D daily achieved 50 ng goal – Jan 2020 |
|
01 Sep, 2020 |
|
Critically Ill or injured patients need 30-50 ng of Vitamin D – Matthews March 2020 |
|
18 Mar, 2020 |
|
Low Vitamin D symptoms, need 50-80 ng, he takes 5,000 IU – Matthews interview Dec 2019 |
|
29 Dec, 2019 |
|
NCAA trainers are getting on board the Vitamin D train (40-50 ng)– Nov 2019 |
|
16 Nov, 2019 |
|
Biology of Vitamin D – 30ng min., 50ng preferred, 1000X lower cost than health problem – Feb 2019 |
|
02 Mar, 2019 |
|
Diabetes 5X less likely if more than 50 ng of Vitamin D – April 2018 |
|
23 Jan, 2019 |
|
Vitamin D is needed for human fertility – goal is 50 ng – Sept 2018 |
|
22 Aug, 2018 |
|
Colorectal cancer 60 percent less likely if have more than 50 ng of vitamin D (vs 5 ng) – meta-analysis April 2017 |
|
09 Aug, 2018 |
|
Korea proposes vitamin D of 20 ng, but notes 20ng increases osteo by 50 percent – Oct 2012 |
|
03 Jul, 2018 |
|
Half of Tianjin China had less than sufficient vitamin D (IoM of 20-50 ng) - June 2018 |
|
04 Jun, 2018 |
|
Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Vitamin D review (needs 40-50 ng) – Feb 2018 |
|
26 Feb, 2018 |
|
Hypertension not controlled by 26 ng of Vitamin D (50,000 IU bi-weekly A-A) – RCT Nov 2017 |
|
18 Nov, 2017 |
|
Hypothyroidism risk reduced 32 percent in those getting vitamin D levels above 50 ng – Oct 2017 |
|
27 Oct, 2017 |
|
Chinese women in tropics needed 50,000 IU of Vitamin D monthly to keep above 30 ng – RCT May 2017 |
|
14 Jul, 2017 |
|
All myopic children had less than 50 ng of vitamin D – March 2016 |
|
06 Apr, 2017 |
|
A group of 6,000 people have vitamin D levels higher than 50 ng – GrassrootsHealth |
|
29 Jun, 2016 |
|
Populations with more than 50 ng of vitamin D |
|
09 Apr, 2016 |
|
Staph infection reduced 50 percent when have more than 30 ng of vitamin D – Aug 2011 |
|
13 Feb, 2016 |
|
Outdoor distance runners had great Vitamin D levels (50 ng) – Dec 2015 |
|
24 Dec, 2015 |
|
Asthma at age 20 increased if vitamin D during pregnancy was higher than 50 ng – Oct 2015 |
|
04 Nov, 2015 |
|
Common cold (Acute Rhinosinusitis) virually non-existant when Vitamin D is above 50 ng – Oct 2015 |
|
13 Oct, 2015 |
|
Sports benefits from up to 50 ng of Vitamin – meta-analysis - Nov 2012 |
|
29 Sep, 2015 |
|
Vitamin D more than 40 ng: 1300 IU 50% chance: 5,000 IU 80% chance - Aug 2014 |
|
13 Sep, 2015 |
|
Many more people now have vitamin D levels above 50 ng, especially seniors – May 2015 |
|
20 Jun, 2015 |
|
Vitamin D video: calcification, narrow-band UV, 4,000 IU, 50 ng – Dr. DeLuca May 2015 |
|
04 Jun, 2015 |
|
50 percent more elderly deaths when vitamin D under 18 ng or over 40 ng – Aug 2010 |
|
31 May, 2015 |
|
Dr. Oz recommends at least 50 ng of vitamin D |
|
20 Mar, 2015 |
|
Dr Oz: 50ng of vitamin D - Nov 2009 |
|
20 Mar, 2015 |
|
Smoking associated with 9 ng less vitamin D age 40-50 – Nov 2014 |
|
24 Nov, 2014 |
|
Semen worse when vitamin D lower than 20 or higher than 50 ng – Oct 2012 |
|
16 Oct, 2014 |
|
Fertility in both women and men improves with more vitamin D (but less than 50 ng for men) – Dec 2013 |
|
16 Oct, 2014 |
|
Pregnant blacks 50 pcnt more likely to be depressed if 3 ng less vitamin D – July 2012 |
|
23 Sep, 2014 |
|
5000 IU vitamin D3 added daily to bread raised blood levels to 50 ng – 2009 |
|
16 May, 2014 |
|
Vitamin D update – 40-60 ng ideal, 50K biweekly maintenance – Jan 2014 |
|
24 Mar, 2014 |
|
Diabetics with 8ng less vitamin D had a 50 percent increase chance of DHCR7 gene variation – Jan 2014 |
|
29 Jan, 2014 |
|
Dr. Oz again recommends at least 50 ng of vitamin D - Dec 2013 |
|
05 Jan, 2014 |
|
50,000 IU of vitamin D monthly in winter gets most above 20 ng – RCT Nov 2013 |
|
21 Dec, 2013 |
|
Dr Oz recommends 50 ng vitamin D blood level |
|
03 Dec, 2013 |
|
50,000 IU vitamin D weekly increased levels by 52 ng normally, but only 28 ng if obese – Oct 2013 |
|
13 Nov, 2013 |
|
At least 5,000 IU Vitamin D to get to optimal 50 ng - LEF Nov 2013 |
|
11 Nov, 2013 |
|
30 to 50 ng of vitamin D is optimal – Central Europe consensus Sept 2013 |
|
23 Sep, 2013 |
|
European Osteo group recommends 20-50 ng of vitamin D – Jan 2013 |
|
17 Jan, 2013 |
|
Probability of knee osteoarthritis up 50 percent if 20 ng less vitamin D – Nov 2011 |
|
10 Nov, 2012 |
|
Metabolic syndrome 50 percent more likely if under 20 ng of vitamin D - May 2011 |
|
23 Jun, 2012 |
|
USANA found 5000 IU resulted in 50 ng - Winter 2010 |
|
24 Sep, 2011 |
|
Vitamin D level of 50 ng may be too high - May 2010 |
|
24 Sep, 2011 |
|
Athletes need 50 ng/ml of Vitamin D – Cannell and Hollis – 2009 |
|
02 Jul, 2011 |